Well-designed Soybean extract Factory from Madras
Well-designed Soybean extract Factory from Madras Detail:
[Latin Name] Glycine max (L.) Mere
[Plant Source] China
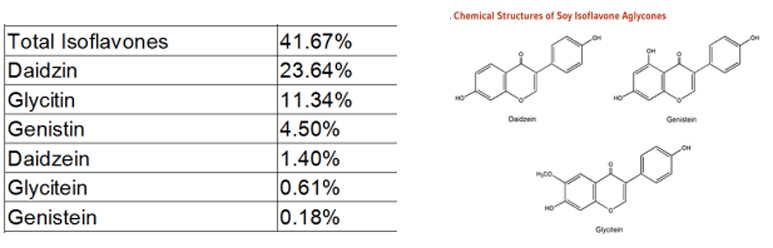
[Specifications] Isoflavones 20%, 40%, 60%
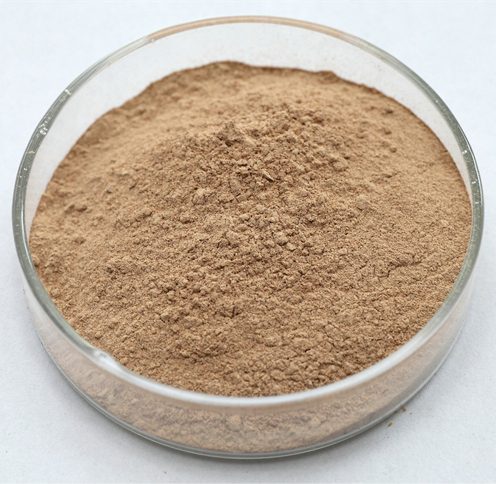
[Appearance] Brown yellow fine powder
[Plant Part Used] Soybean
[Particle size] 80 Mesh
[Loss on drying] ≤5.0%
[Heavy Metal] ≤10PPM
[Storage] Store in cool & dry area, keep away from the direct light and heat.
[Package] Packed in paper-drums and two plastic-bags inside.
[Active ingredients]
[What is Soy Isoflavones]
Non-genetically modified soybean refined soy isoflavones, a natural nutritional factors for a variety of important physiological activity is a natural plant estrogen, easily absorbed by the body.
Isoflavones are phytoestrogens planned economy a weak hormones, soy is the only valid source of human access to isoflavones. In the case of strong estrogen physiological activity, isoflavones can play the role of anti-estrogen. Isoflavones very prominent anti-cancer properties, can hinder the growth and spread of cancer cells and only cancer, isoflavones had no impact on normal cells. Isoflavones has an effective of anti-oxidant.
[Functions]
1. Lower Cancer Risk In Men and Women;
2. Use In Estrogen Replacement Therapy;
3. Lower Cholesterol and Reduce Heart Disease Risk;
4. Relieve women menopause syndrome, guard against osteoporosis;
5. Protect human body from destroy by free-radical to advance immunity;
6. Be healthy for stomach and spleen and protect nerve system;
7. Reduce cholesterin thickness in human body, prevent and cure cardiovascular disease;
8. Prevent cancer and counteract cancer£¬for example, prostate cancer, breast cancer.
[Application] Used in Lower cancer risk, estrogen replacement therapy, advance immunity, prevent and cure cardiovascular disease.
Product detail pictures:

Related Product Guide:
We also provide item sourcing and flight consolidation solutions. We have now our very own manufacturing facility and sourcing place of work. We could provide you with nearly every kind of merchandise associated to our merchandise variety for Well-designed Soybean extract Factory from Madras , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Bangalore, India, Mexico, Satisfaction and good credit to every customer is our priority. We focus on every detail of order processing for customers till they have received safe and sound solutions with good logistics service and economical cost. Depending on this, our solutions are sold very well in the countries in Africa, the Mid-East and Southeast Asia.
Hey you guys! This is my Wash ‘N Go using the new Eco styler Castor & Flaxseed Oil, I actually found a review of a woman talking about her hair fell out…Sis, your hair was prolly already falling out cause this gel is literally the GOAT!
PRODUCTS USED!
Shampoo/Conditioner- Hask Monoi Coconut oil
Leave in Conditioner- Jamaican castor oil & taliah waajid coconut spray
Hope you guys like it! Like & Subscribe for more videos! ![]()
Social Media:
IG(Main): sakina.247
IG(Hair): sakinasbeauty
SC: jamaisx
Email: leturah13@gmail.com
https://davesmith.ludaxx.com
https://www.davegsmith.com/
https://bluelineproducts.com/
Why it Functions for over the counter appetite suppressant in this area El Paso
When it Functions for
F21 is an All Natural Sugar Blocker that assists restrict your blood sugar absorption. It consists of various substances found to have numerous wellness advantages, such as L-Arabinose, Coriolus Versicolor Polysacchride, Konjac-Mannan, Magnesium Stearate, Mint flavor: Menthol and Natural Colors. F21 not just does it help advertise weight management, (PSK) boosts your immune system feedback. In fact, for every gram of F21, you can obstruct up to 20 grams of sugar (sucrose). The formula not just assists advertise weight management, it rewards the digestion system by enabling the blocked sucrose to support helpful probiotic germs while the polysaccharide (PSK) boosts your immune system feedback.
DG Smith https://www.davegsmith.com/
over the counter appetite suppressant :
00:00:05 loose weight
00:00:11 controlling hunger
00:00:17 over the counter diet pills
00:00:23 controlling hunger
00:00:29 how to control sugar diabetes
We are really happy to find such a manufacturer that ensuring product quality at the same time the price is very cheap.