Bottom price for Ginseng extract Supply to Pakistan
Bottom price for Ginseng extract Supply to Pakistan Detail:
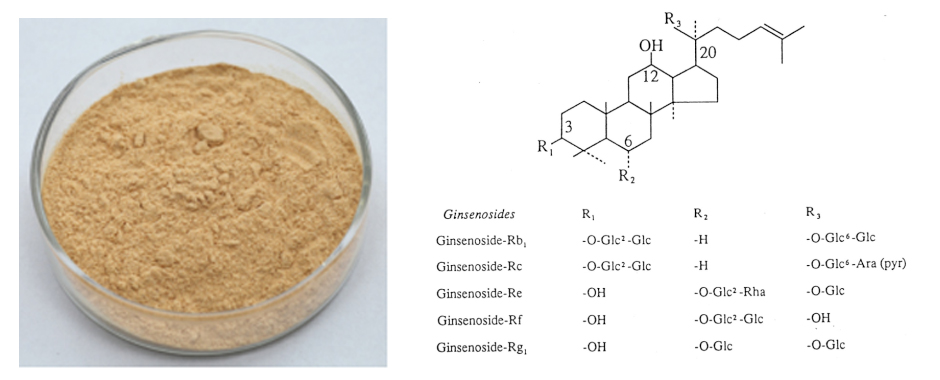
[Latin Name] Panax ginseng CA Mey.
[Plant Source] Dried Root
[Specifications] Ginsenosides 10%–80%(UV)
[Appearance] Fine Light Milk Yellow Powder
[Particle size] 80 Mesh
[Loss on drying] ≤ 5.0%
[Heavy Metal] ≤20PPM
[Extract solvents] Ethanol
[Microbe] Total Aerobic Plate Count: ≤1000CFU/G
Yeast & Mold: ≤100 CFU/G
[Storage] Store in cool & dry area, keep away from the direct light and heat.
[Shelf life]24 Months
[Package] Packed in paper-drums and two plastic-bags inside.
[What is Ginseng]
In terms of modern scientific research, ginseng is known to be an adaptogen. Adaptogens are substances that assist the body to restore itself to health and work without side effects even if the recommended dose is widely exceeded.
Ginseng due to its adaptogens effects is widely used to lower cholesterol, increase energy and endurance, reduce fatique and effects of stress and prevent infections.
Ginseng is one of the most effective antiaging supplements. It can alleviate some major effects of aging, such as degeneration of the blood system, and increase mental and physical capacity.
Other important benefits of ginseng is its support in cancer treatment and its effects on sports performance.
[Application]
1. Applied in food additives, it owns the effect of antifatigue, anti-aging and nourishing brain;
2. Applied in pharmaceutical field, it is used to treat coronary heart disease, angina cordis, bradycardia and high heart rate arrhythmia, etc.;
3. Applied in cosmetics field, it owns the effect of whitening, dispelling spot, anti-wrinkle, activating skin cells, making skin more tender and firm.
Product detail pictures:

Related Product Guide:
Our company insists all along the quality policy of "product quality is base of enterprise survival; customer satisfaction is the staring point and ending of an enterprise; persistent improvement is eternal pursuit of staff" and the consistent purpose of "reputation first, customer first" for Bottom price for Ginseng extract Supply to Pakistan , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: UK, Chile, America, With excellent solutions, high quality service and sincere attitude of service, we ensure customer satisfaction and help customers create value for mutual benefit and create a win-win situation. Welcome customers all over the world to contact us or visit our company. We'll satisfy you with our qualified service!
Hey guys I roasted pumpkin seeds!! This is a LIGHTLY seasoned recipe if you want to add more sugar or cinnamon you can! If you have more pumpkin seeds than double the amount. I know some of us have lots of pumpkins left over. Mines were sitting there getting OLD!! I am making puree with the actual pumpkin yum!
You can also make salty and spicy ones if you want YUM!
Thanks for watching XOXO
In this lecture i m discuss about the introduction of carbohydrates. carbohydrates means hydrates of carbon. A carbohydrate is a biological molecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water); in other words, with the empirical formula Cm(H2O)n (where m could be different from n). This formula holds true for monosaccharides. Some exceptions exist; for example, deoxyribose, a sugar component of DNA, has the empirical formula C5H10O4. Carbohydrates are technically hydrates of carbon; structurally it is more accurate to view them as polyhydroxy aldehydes and ketones.
The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of ‘saccharide’, a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular weight) carbohydrates, are commonly referred to as sugars.The word saccharide comes from the Greek word σάκχαρον (sákkharon), meaning “sugar”. While the scientific nomenclature of carbohydrates is complex, the names of the monosaccharides and disaccharides very often end in the suffix -ose. For example, grape sugar is the monosaccharide glucose, cane sugar is the disaccharide sucrose, and milk sugar is the disaccharide lactose.
Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. Polysaccharides serve for the storage of energy (e.g. starch and glycogen) and as structural components (e.g. cellulose in plants and chitin in arthropods). The 5-carbon monosaccharide ribose is an important component of coenzymes (e.g. ATP, FAD and NAD) and the backbone of the genetic molecule known as RNA. The related deoxyribose is a component of DNA. Saccharides and their derivatives include many other important biomolecules that play key roles in the immune system, fertilization, preventing pathogenesis, blood clotting, and development.
In food science and in many informal contexts, the term carbohydrate often means any food that is particularly rich in the complex carbohydrate starch (such as cereals, bread and pasta) or simple carbohydrates, such as sugar (found in candy, jams, and desserts).
Often in lists of nutritional information, such as the USDA National Nutrient Database, the term “carbohydrate” (or “carbohydrate by difference”) is used for everything other than water, protein, fat, ash, and ethanol. This will include chemical compounds such as acetic or lactic acid, which are not normally considered carbohydrates. It also includes “dietary fiber” which is a carbohydrate but which does not contribute much in the way of food energy (calories), even though it is often included in the calculation of total food energy just as though it were a sugar.
Carbohydrates are found in a wide variety of foods. The important sources are cereals (wheat, maize, rice), potatoes, sugarcane, fruits, table sugar(sucrose), bread, milk, etc. Starch and sugar are the important carbohydrates in our diet. Starch is abundant in potatoes, maize, rice and other cereals. Sugar appears in our diet mainly as sucrose(table sugar) which is added to drinks and many prepared foods such as jam, biscuits and cakes. Glucose and fructose are found naturally in many fruits and some vegetables. Glycogen is carbohydrate found in the liver and muscles (as animal source). Cellulose in the cell wall of all plant tissue is a carbohydrate. It is important in our diet as fiber which helps to maintain a healthy digestive system.
oligosaccharide,polysaccharide biology,polysaccharides,carbohydrate metabolism,CARBOHYDRATES,carbohydrate in hindi,carbohydrates classification,Carbohydrates (Hindi),CLASSIFICATION OF CARBOHYDRATES,Super Revision- Carbohydrates,Introduction & classification of carbohydrates, Carbohydrates & Sugars, CARBOHYDRATES LECTURE , Biochemistry of Carbohydrates, monosaccharide, vinay, vinay rajput, vinay rajput tutorial, introduction of carbohydrates, carbohydrates by vinay rajput carbohydrates by vinay, carbohydrates in hindi, carbohydrates food list in hindi, carbohydrates food list india, carbohydrates food, carbohydrates food list , carbohydrates biochemistry in hindi, carbohydrates biochemistry, carbohydrates biochemistry lecture, carbohydrates biochemistry animation, what are carbohydrates, carbohydrates lipids and proteins. All About Carbohydrates in 6 min! From a HighSchool Student – BIOLOGY | HD Carbohydrates Bozeman science
I describes and gives examples of monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharide and polysaccharides. I also explains how they grow through dehydration reactions and shrink through hydrolysis.
Products and services are very good, our leader is very satisfied with this procurement, it is better than we expected,