15 Years Manufacturer Curcuma Longa Extract Factory for Angola
15 Years Manufacturer Curcuma Longa Extract Factory for Angola Detail:
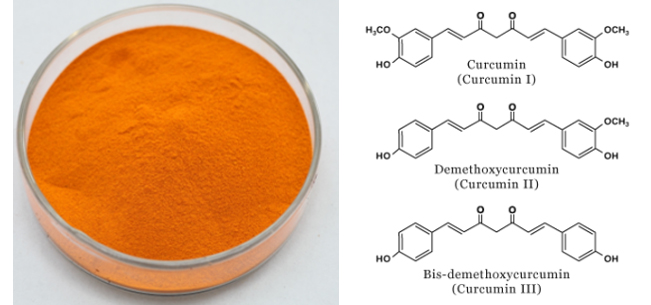
[Latin Name] Curcuma longa L.
[Plant Source] Root From India
[Specification] Curcuminoids 95% HPLC
[Appearance] Yellow powder
Plant Part Used: Root
[Particle size]80Mesh
[Loss on drying] ≤5.0%
[Heavy Metal] ≤10PPM
[Storage] Store in cool & dry area, keep away from the direct light and heat.
[Shelf life] 24 Months
[Package] Packed in paper-drums and two plastic-bags inside.
[Net weight] 25kgs/drum
[What is Curcuma Longa?]
Turmeric is an herbaceous plant known scientifically as Curcuma longa. It belongs to the Zingiberaceae family, which includes ginger. Tumeric has rhizomes rather than true roots, which are the primary source of commercial value for this plant. Tumeric originates from southwest India, where it has been a stable of Siddha medicine for thousands of years. It is also a common spice in Indian cuisine and is often used as flavoring for Asian mustards.
Product detail pictures:

Related Product Guide:
Our business puts emphasis on the administration, the introduction of talented personnel, as well as the construction of team building, trying hard to further improve the standard and liability consciousness of staff members customers. Our enterprise successfully attained IS9001 Certification and European CE Certification of 15 Years Manufacturer Curcuma Longa Extract Factory for Angola , The product will supply to all over the world, such as: Poland, Brunei, Congo, With the growing of the company, now our products sold and served at more than 15 countries around the world,such as Europe,North America,Middle-east,South America,Southern Asia and so on. As we bear in our mind that innovation is essential to our growth, new product development is constantly.Besides, Our flexible and efficient operation strategies,High quality products and competitive prices are exactly what our customers are looking for. Also a considerable service brings us good credit reputation.
endlessly living items y crimson camacho presentan Bee Pollen.siguenos en www.foreverlivingmexico.internet y tendras mucha informacion.
Hey guys I roasted pumpkin seeds!! This is a LIGHTLY seasoned recipe if you want to add more sugar or cinnamon you can! If you have more pumpkin seeds than double the amount. I know some of us have lots of pumpkins left over. Mines were sitting there getting OLD!! I am making puree with the actual pumpkin yum!
You can also make salty and spicy ones if you want YUM!
Thanks for watching XOXO
Sales manager is very enthusiastic and professional, gave us a great concessions and product quality is very good,thank you very much!